CE marking indicates that a product is declared by the manufacturer as in conformity with Union harmonisation legislation and enables the free movement of products within the European market.
- Legal mandatory requirement
- Trade Passport: Free commercial movement in EEA
- It must be affixed according to its legal format visibly, legibly and indelibly to the product or its data plate.
- The products which meet all the applicable directives must be CE marking
It guarantees:
- Compliance with essential requirements of EU technical regulations (Directives)
- That compliance has been demonstrated throughout relevant conformity assessment procedures
By affixing the CE Marking the manufacturer declares on his sole responsibility that the product conforms to all applicable Union legislative requirements, and that the appropriate conformity assessment procedures have been successfully completed.
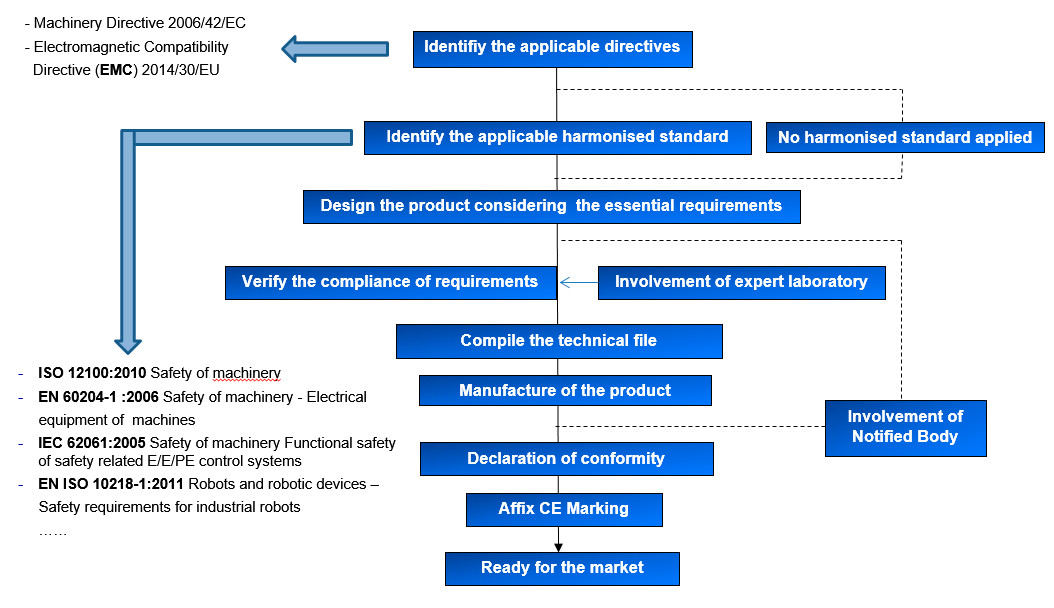
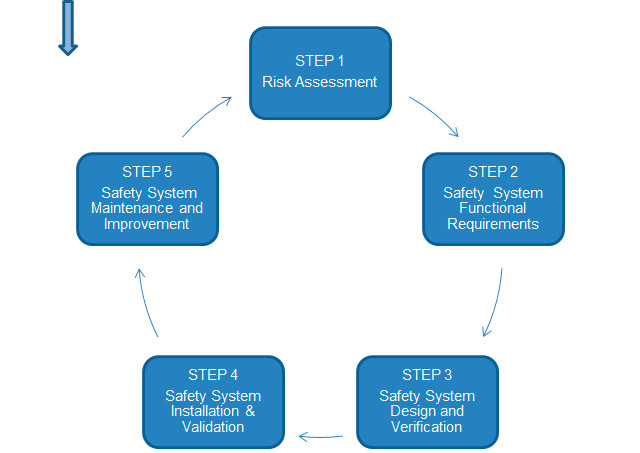
Following, the required steps in order to get a safe robot are set forth. It should be pointed out that it is necessary to consider not only the appropriate robot design but also the robot application and the different scenarios where it will work.
Standard procedure for Robots CE MARKING Management
Alter Technology is able to support your company during the whole CE marking process.
Safe Robot Design
ISO 12100:2010
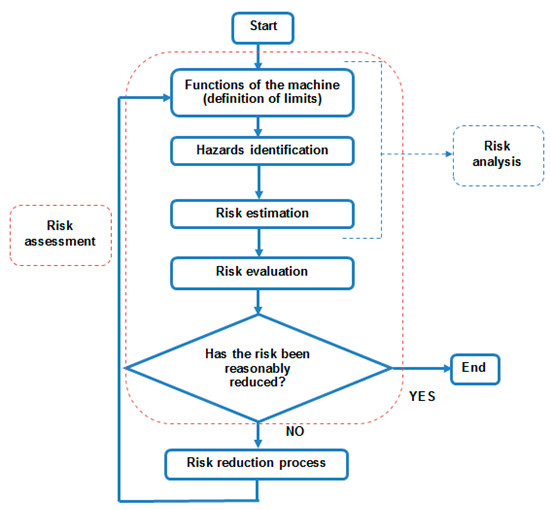
ISO 12100:2010 Safety of machinery — General principles for design — Risk assessment and risk reduction
Risk analysis
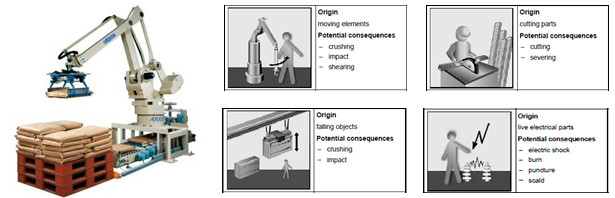
HAZARD: Potential source of harm
Mechanical hazards Noise hazards
Electrical hazards Vibration hazards
Thermal hazards Radiation hazards ….
RISK = Probability of ocurrence of harm * Severity of that harm
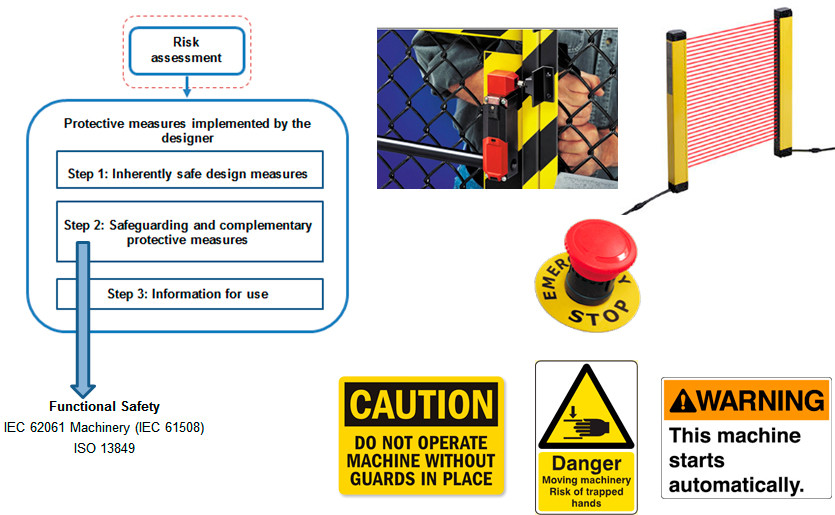
Risk assessment
Functional Safety
- Part of the overall safety relating to the Equipment Under Control (EUC) and the equipment control systems that depends on a system operating correctly in response to its inputs.
- What has to be performed?
- From the hazard analysis ⇒ Safety function requirement.
- What degree of certainty is necessary so that the safety function will be performed safisfactorily.
- From the risk assessment ⇒ Safety integrity requirement.
- Functional safety is achieved designing a Safety-Related System (SRS) to carry out a Safety Function at a reliability indicated by the Safety Integrity Level (SIL).
IEC 61508: A standard in seven parts
- Functional safety of electrical/electronic/programmable electronic (E/E/PE) safety-related systems.
- An (E/E/PE) safety-related systems covers all parts of the system which are necessary to carry out the safety function:
Sensor ⇒ Logic ⇒ Actuator
- IEC 61508: Three safety lifecycles to manage all product phases