LEDs & Photodiodes
LED Technologies & Properties
- LED is a two-lead semiconductor light source. LEDs are small and are commonly used as indicator lamps in electronic devices
- Due to the increased design flexibility, efficient use of power and environmental benefits the use of LEDs as lighting, data communication and signalling devices is growing in many applications such as space, aviation and automotive lighting, advertising and traffic signals
- The use of new semiconductor compounds based on GaN, GaP, InP and GaAs allows to cover a wider light-emitting range

Key performance parameters
- Radiant flux
- Spectral response
- Forward voltage
- Emission angle
- Reverse current

PHOTODIODE TECHNOLOGIES & PROPERTIES
- A photodiode is a two-lead semiconductor light detector that converts light into electric current (i.e. photocurrent). The generated photocurrent can be quite precisely proportional to the incident light
- The semiconductor material used to make a photodiode is critical to defining its properties, it should have a strong absorption for the optical wavelength of interest
- Semiconductor compounds based on Si, Ge, InP, GaN and InGaAs materials allow to have good detection sensitivity in wide spectral range
Critical performance parameters
- Spectral responsivity
- Dark current
- Response time
- NEP
- Bandwidth

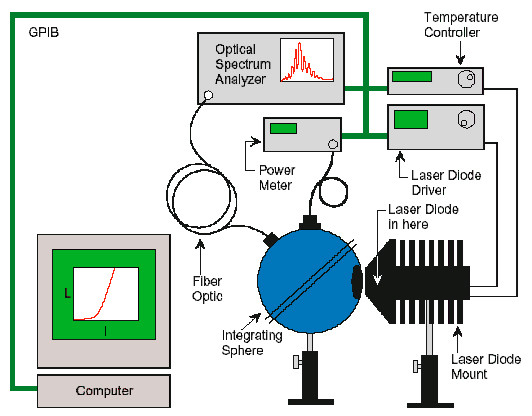
Integrating sphere setup
Latest posts by Laura Peñate (see all)
- LED Technologies & Properties - 2nd February 2016
- Fast optical source for quantum key distribution based on semiconductor optical amplifiers - 1st February 2016
- Low Temperature Radiation Test of High Voltage Optocouplers for Space Applications - 1st February 2016