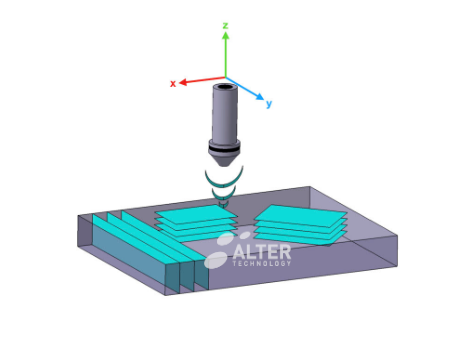
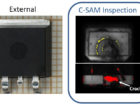
In acoustic microscopy, resolution and inspection depth are inversely related parameter that depend on the probe frequency and the characteristics of the involved materials. Therefore, the inspection frequency must to be carefully selected in order to optimize the accuracy without decreasing the inspection depth below the specimen thickness. Suitable selection of the inspection parameters provides:
- Detection of ultra-thin (submicrometric) delamination in multilayer systems.
- Micrometric lateral resolution.
In addition, the technique permits the internal inspection of different cutting planes (non-destructive virtual cross-section) and the simultaneous analysis of defects and interfaces at different depths. This provides the technique with in-depth multifocal inspection capabilities which in turn are used for the tomographic 3D reconstruction of complex internal structures.
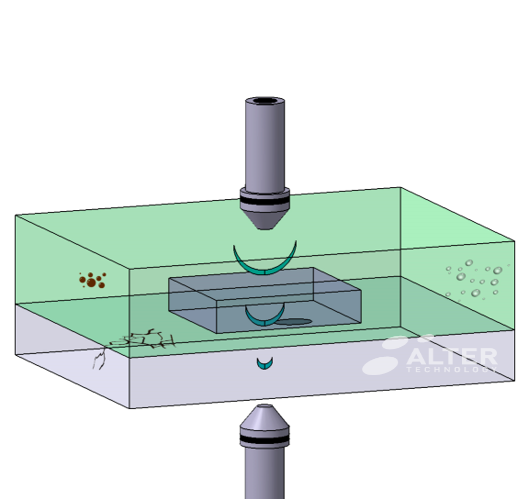
Confocal inspection (C-Scan mode)
This scanning mode analyses the internal structure at a fixed depth within a selected thickness. By this way, it generates a stratified image of the component. In the resulting image, the higher intensity of the acoustic waves reflected at air interfaces and defects provides a clear contrast. Thus, this scan mode is particularly sensitive to air voids and delaminations; and permit the defection sub-micrometric-thick features.
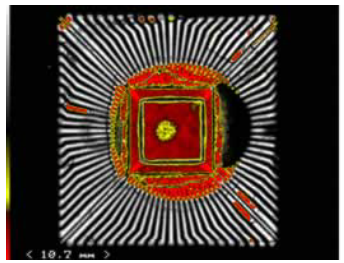
Through-transmission mode (Th-Scan mode)
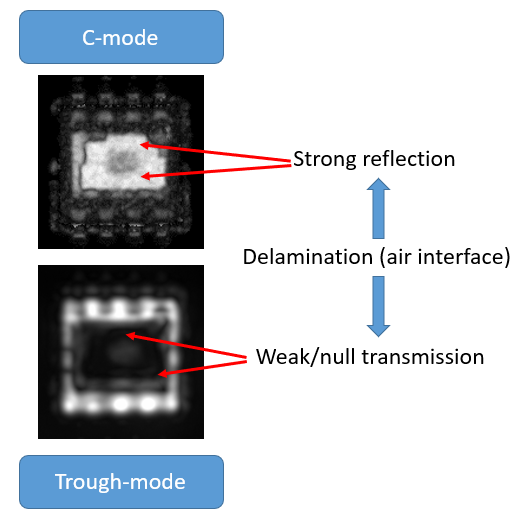
Through-transmission mode (Th-Scan mode) is a scan mode that analyses the intensity of the ultrasound beam that propagates through the entire thickness of the sample. This scan mode is used for the thorough inspection of the whole system in a single scan. In addition, this inspection complementary to confocal reflection analyses (C-SAM) is very effective in the detection of hidden defects at the die attach and to confirm the interpretation of C-SAM findings. The image below compares C-SAM and Th-SAM images simultaneously acquired. This comparison shows how the delaminated areas produce a strong reflection (very bright zones in the CSAM image) and low intensity in the transmitted signal.
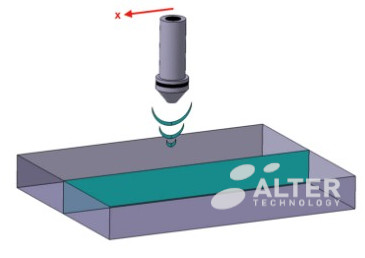
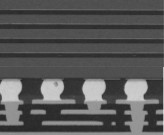
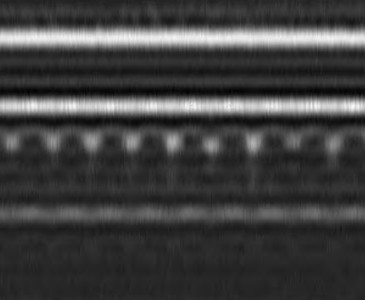
Virtual cross-section (B-Scan mode)
In this case the system combines multi-depth analyses sequentially conducted along a given line to reconstruct a depth resolved cross section image as the one in the figure.
Multi-focus inspection (X-Scan mode)
For multi-focus inspection purposes the system accumulates several C-scans simultaneously registered at selected depths. This allows us to inspect different materials and interfaces within a single scan process.
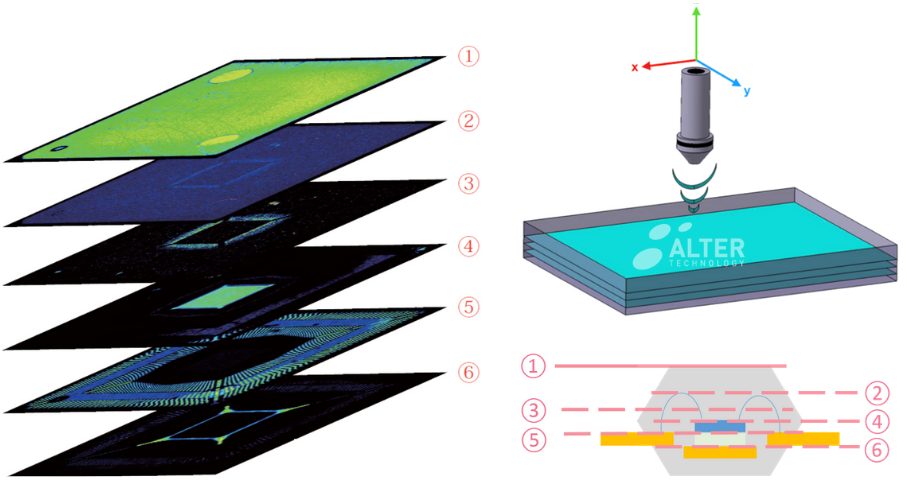
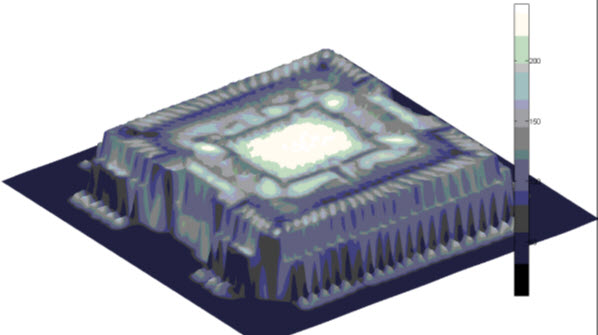
3D Tomography (Z-Scan mode)
The 3-dimensional information acquired in X-scans permit the tomographic reconstruction of the system internal structure.
- Scanning Acoustic Microscopy on Ceramic Capacitors - 18th May 2020
- Non-destructive detection of micrometric internal features within EEE microelectronic systems. - 3rd September 2019
- Acoustic Inspection of Hybrid Systems on Laminated Substrates - 3rd September 2019